Access control»
Spaces provide the organizational structure for Spacelift's role-based access control (RBAC) system. Permission management is handled through login policies or user management depending on your authorization strategy. All roles are assigned to specific spaces, providing precise control over who can access what resources.
Roles and RBAC»
System roles»
Spacelift provides several built-in system roles roles that can be assigned to users on a space-by-space basis:
- Space Reader: View-only access to resources within the space, can add comments to runs for collaboration.
- Space Writer: Space Reader permissions + ability to trigger runs and modify environment variables.
- Space Admin: Space Writer permissions + ability to create and modify stacks and attachable entities.
Custom roles»
Beyond predefined roles, you can create custom roles with precisely tailored permissions:
- Granular actions: Compose roles from specific actions like
run:trigger,stack:manage,context:read. - Business-aligned: Match roles to your organizational structure and job functions.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant exactly the permissions needed, nothing more.
Custom Role Example
Instead of giving someone full Space Admin access, create a custom "Infrastructure Developer" role with just:
space:read: View space contentsstack:read: Understand configurationsrun:trigger: Deploy changesrun:read: Monitor deployments
A "Root Space Admin" is a user given administrative permissions to the root space, which is the top-level space in Spacelift's hierarchy. This grants special permissions and allows them to manage the entire account, including modifying the space tree and accessing account-wide settings.
Role permissions»
| Action / Role | Root Space Admin | Space Admin | Space Writer | Space Reader |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Set up SSO | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Set up VCS | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Manage Sessions | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Manage Login Policies & User Management Controls | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Manage Audit Trails | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Invite/Revoke Users | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Create/Modify/Delete Roles | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Create/Modify/Delete API Keys, IdP Group Mappings | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| View Roles, Users, API Keys, IdP Group Mappings | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Manage Role Bindings | ✅ | ✅* | ❌ | ❌ |
| Manage Spaces | ✅ | ✅** | ❌ | ❌ |
| Manage Stack Config Settings | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Manage Worker Pools, Contexts | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Manage Stack Env Vars | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Trigger runs | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| View Stacks | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| View Spaces | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| View Worker Pools, Contexts | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
*Can only manage role bindings for assigned space(s)
**Can only manage assigned space(s)
Authorization methods»
User management»
The user management interface provides a way to assign roles to users, groups, and API keys:
- Click your name in the bottom-left of the screen, then Organization settings.
- In the Identity Management section, select Users, IdP group mapping, or API keys.
- Assign predefined or custom roles to specific spaces.
See assigning roles to users for detailed instructions.
Login policies (policy-as-code)»
Login policies can only be created in the root space. Therefore, only root and legacy space admins and stacks with root space admin roles can modify login policies.
Login policies enable programmatic role assignment using OPA/Rego:
Getting role slugs
To use custom roles in login policies, copy the role slug from Organization Settings → Access Control Center → Roles → select role → copy slug.
Use the roles rule to assign RBAC roles in login policies:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | |
If a user is logged in, their access levels will not change, so newly added spaces might not be visible. The user must log out and back in to see new spaces they're granted access to.
However, the space's creator immediately has access to it.
Inheritance»
Inheritance is a toggle that defines whether a space inherits resources from its parent space or not. When set to true, any stack in the child space can use resources (such as worker pools or contexts) from the parent space. If a space inherits from a parent and its parent inherits from the grandparent, then the space inherits from the grandparent as well.
Inheritance also modifies how roles propagate between spaces:
- If inheritance between spaces is disabled, the roles are propagated only down the space tree.
- If inheritance is enabled, a user with any role in the child space also gets the Read role in the parent space.
Inheritance diagram»
The user in this diagram was given these roles via login policies:
- Read in
read access space. - Write in
write access space. - Admin in
admin access space.
Solid lines indicate where inheritance is enabled, while dashed lines indicate where inheritance is disabled.
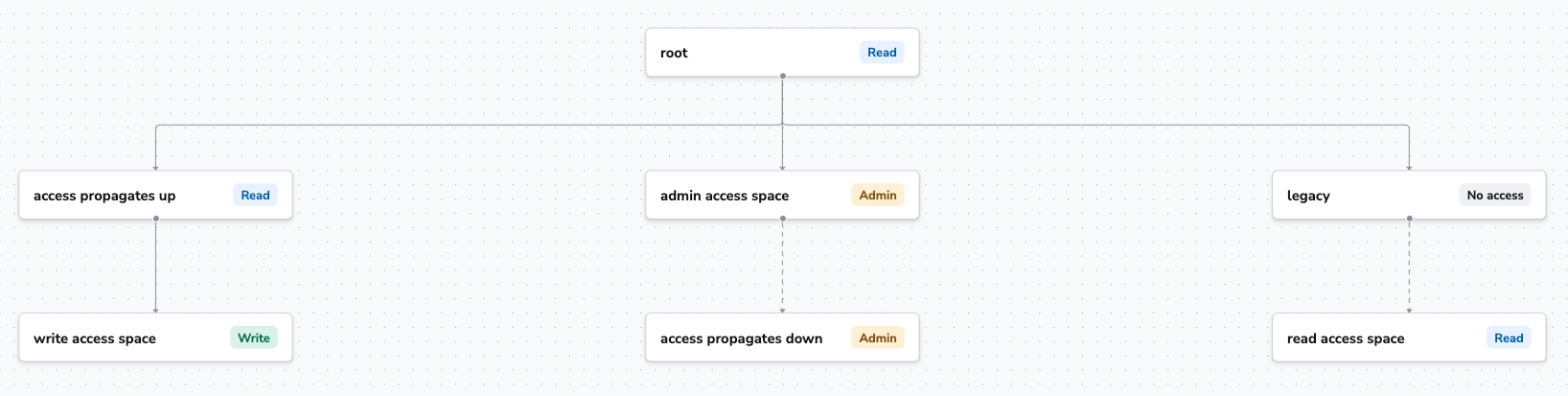
Let's analyze the tree starting from the left.
write access space: The user was granted Write access. Because inheritance is enabled, they also received Read access to theaccess propagates upspace and therootspace, which allows the user to see the resources they can use from the parent spaces.admin access space: The user was granted Admin access. Even though inheritance is disabled, they also received Admin access to theaccess propagates downspace because we want admins to be able to manage their spaces subtree, even if they want to disable resource sharing between some spaces.read access space: The user was given Read access. Because inheritance is disabled, they did not receive any access (read or write) to thelegacyspace.
Related topics»
- Authorization & RBAC: Complete guide to Spacelift's authorization system.
- RBAC System: Understanding roles, actions, and actors.
- User Management: GUI-based permission management.
- Login Policies: Policy-as-code authorization.